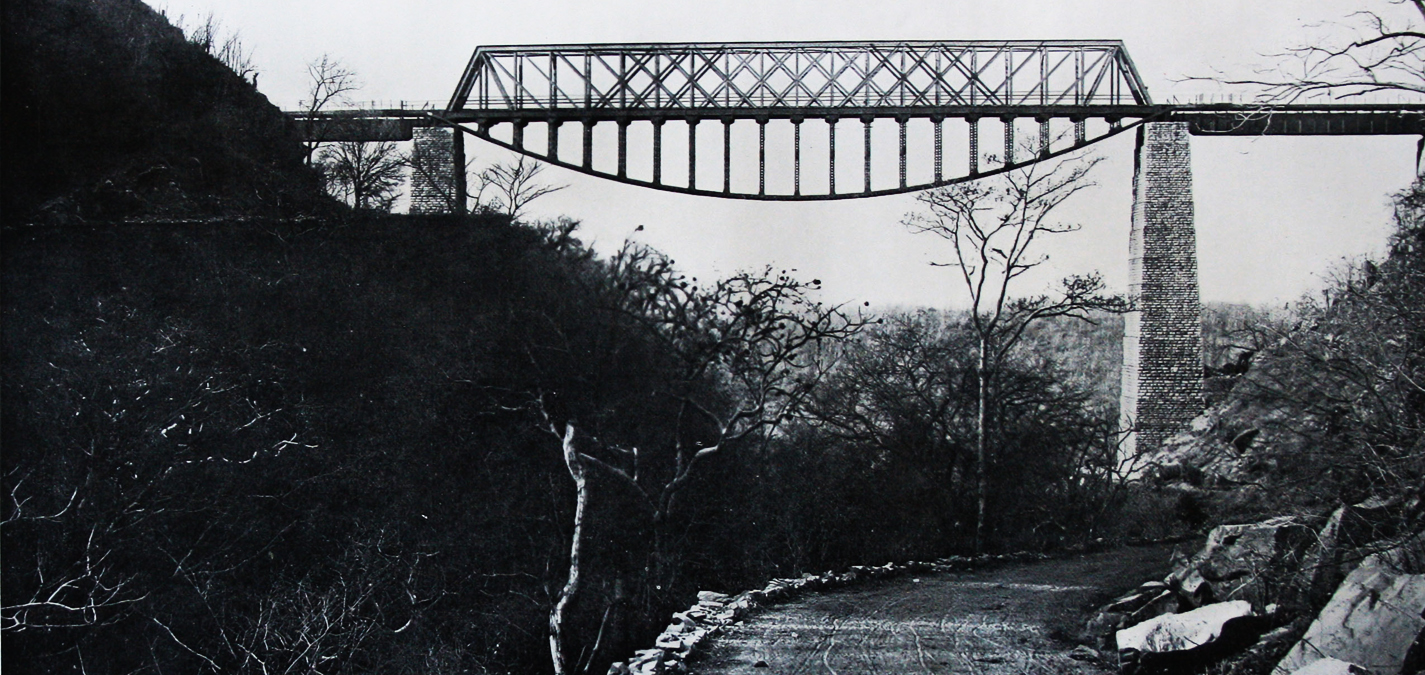
Dorabavi Bridge
Dorabavi Bridge is located in the Nallamala forests of Andhra and Telangana. It is located at Bogada Tunnel on the way from Nandyal to Giddaluru. In 1962, the British government conducted a survey to establish a meter gauge railway line for transporting the goods from Goa to Machilipatnam. The railway line to Guntakal was laid by 1967 after the completion of the survey. The English then wanted to build a railway bridge connecting the valleys in the ebony forests. It is then Dorabavi Bridge came into existence and constructed at a height of 260 feet above sea level and at a distance of 30 km from Nandyala railway station.
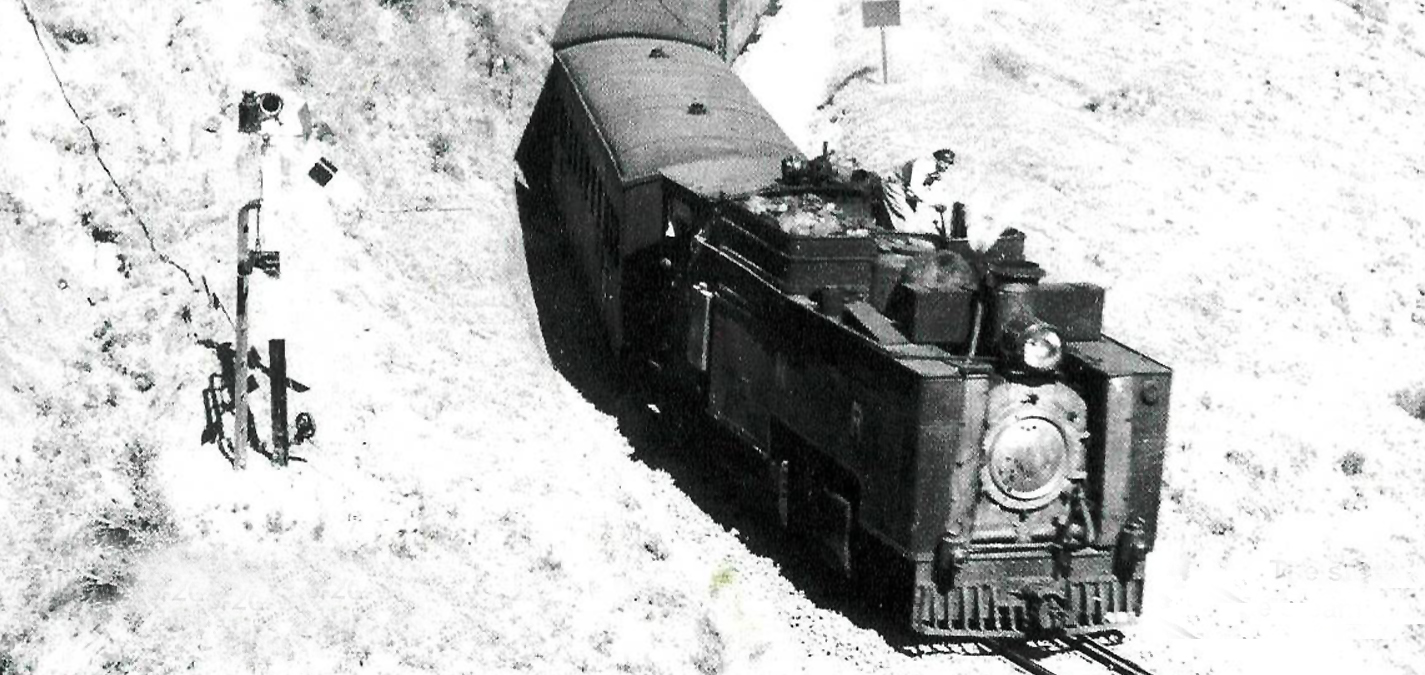

Kalka Shimla Railway
Kalka Shimla Railway (KSR), 96.6 kilometer long, a single track working rail link was built by the Britishers in 1903. This 2ft 6inch narrow-gauge railway was constructed to provide services to the highland town of Shimla, the then summer capital of British Indian rail network. It is known for dramatic views of the hills and surrounding villages on mountainous route from Kalka to Shimla. In 2008, UNESCO added the Kalka Shimla Railway as an extension to the World Heritage Sites of Nilgiri Mountain Railway and Darjeeling Himalayan Railway.
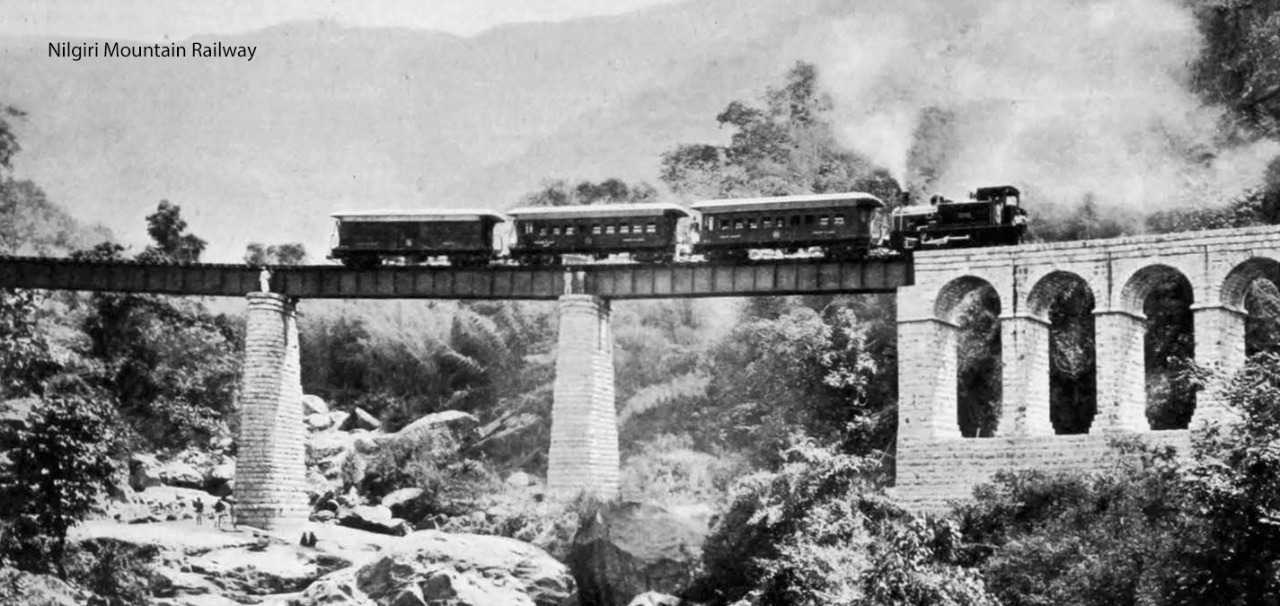

Nilgiri Mountain Railways
The Nilgiri Mountain Railway (NMR) is a 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3/8 in) metre gauge railway in southern regions of India. It is considered to be only rack and pinion railway in India. In 1854, plans were made to build a mountain railway from Mettupalayam to the Nilgiri Hills. The line was completed and opened for traffic in June 1899. It was operated first by the Madras Railway Company which continued to manage the railway line on behalf of the government for a long time until the South Indian Railway company purchased it. In July 2005, UNESCO added the Nilgiri Mountain Railway as an extension to the World Heritage Site of Darjeeling Himalayan Railway. The site then recognized as Mountain Railways of India.
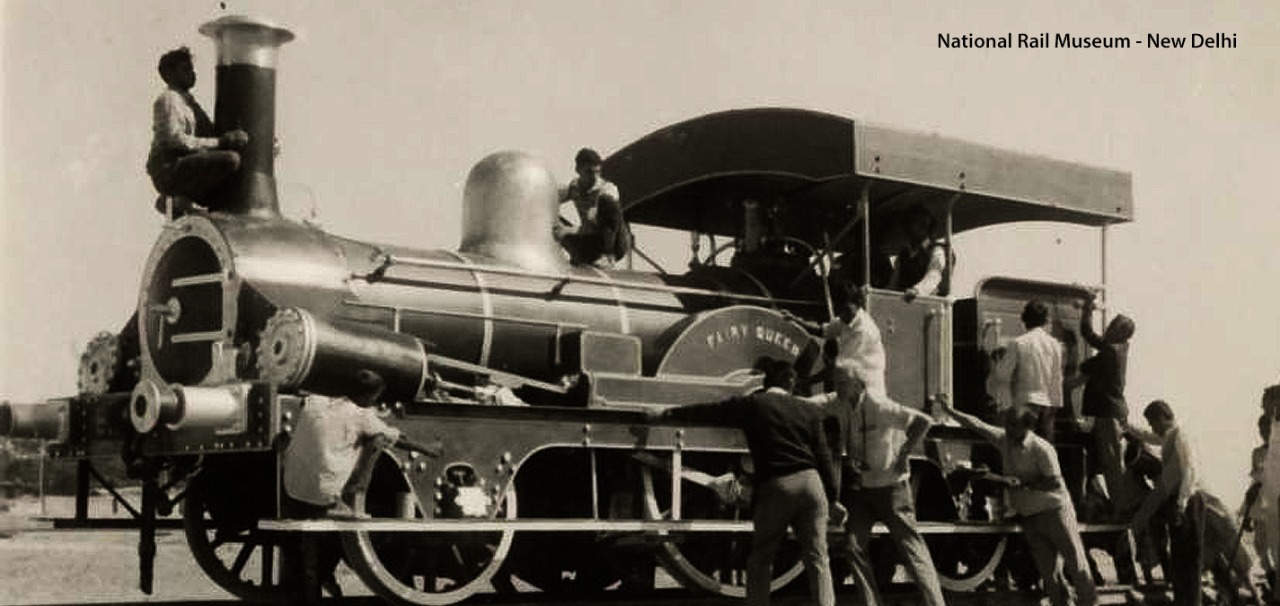

Fairy Queen at National Rail Museum
The Fairy Queen, also known as the East Indian Railway No. 22, is a steam locomotive which was built in the year 1855. It was in service until 1908. The Indian government bestowed heritage status on the Fairy Queen in 1972, rendering it a national treasure. In the image, this prestigious pristine beauty graced and given special spot at the newly built National Rail Museum, New Delhi (1977) and currently housed at the Rewari Heritage Steam Shed. Fairy queen was restored by Loco Works Perambur, Chennai and rolled again on 1st Feb, 1997 from Delhi to Alwar. It was accredited by the Guinness Book of Records in 1998 as the world's oldest steam locomotive in regular operation. Later, in 1999, she received a National Tourism Award for the most innovative and unique tourism project.

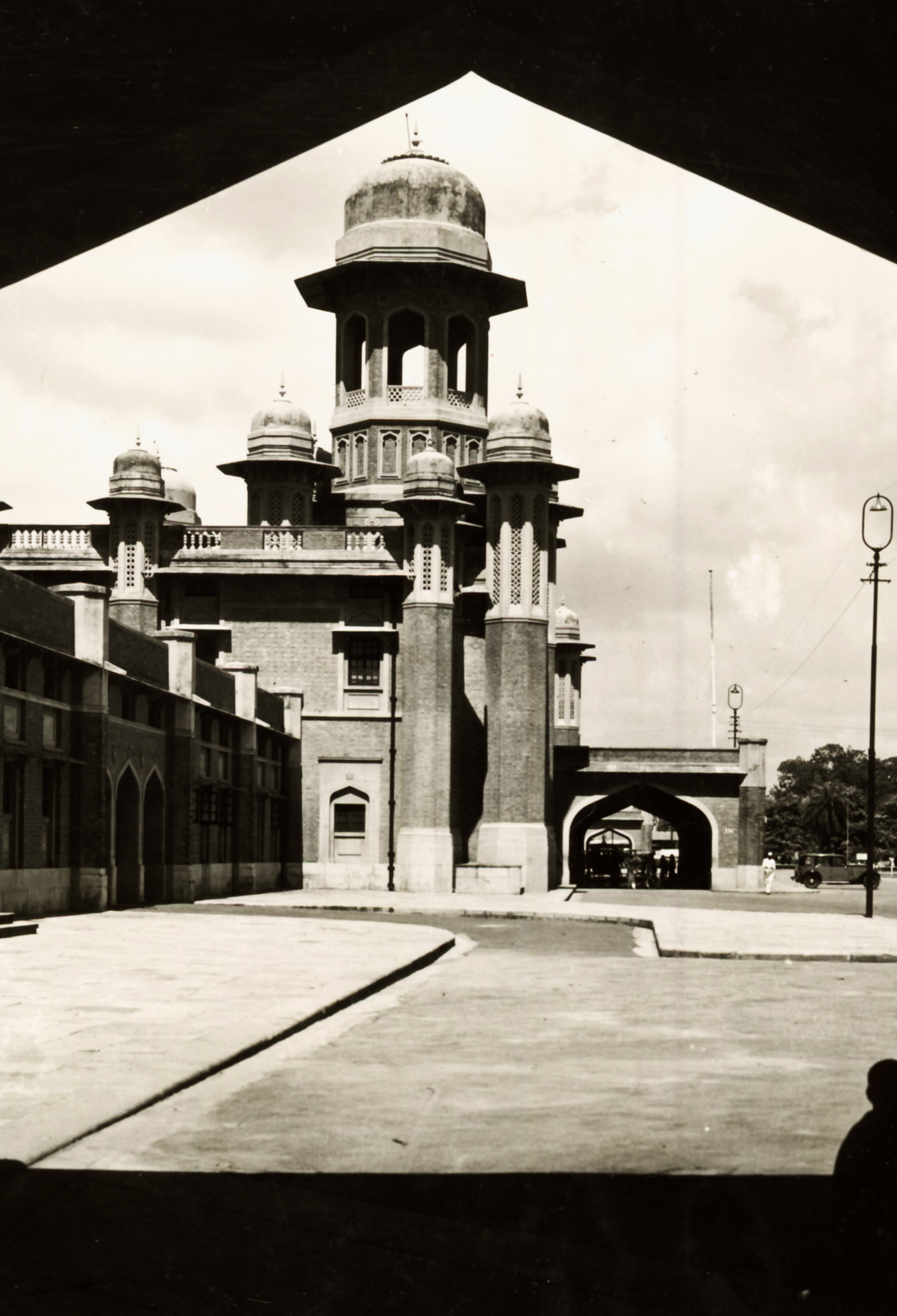
National Rail Museum
In Indian Railways, the history was created on 7th October, 1971, when the then President of India, Shri V.V. Giri laid the foundation stone for the first ever Transport Museum in India. The Transport Museum was planned to exhibit the vast history and rich heritage of Railways, Roadways, Airways and Water-ways in India, which later on developed into a fully fledged National Rail Museum. It covers a land area of over 11 acres comprising of elegantly designed octagonal building i.e., indoor gallery and more than 90 real size exhibits which includes locomotives, saloons, wagons, etc. This museum promises to take its visitors on an exciting journey into the history, heritage and contribution made by Indian Railways to industrial and economic progress of the nation.
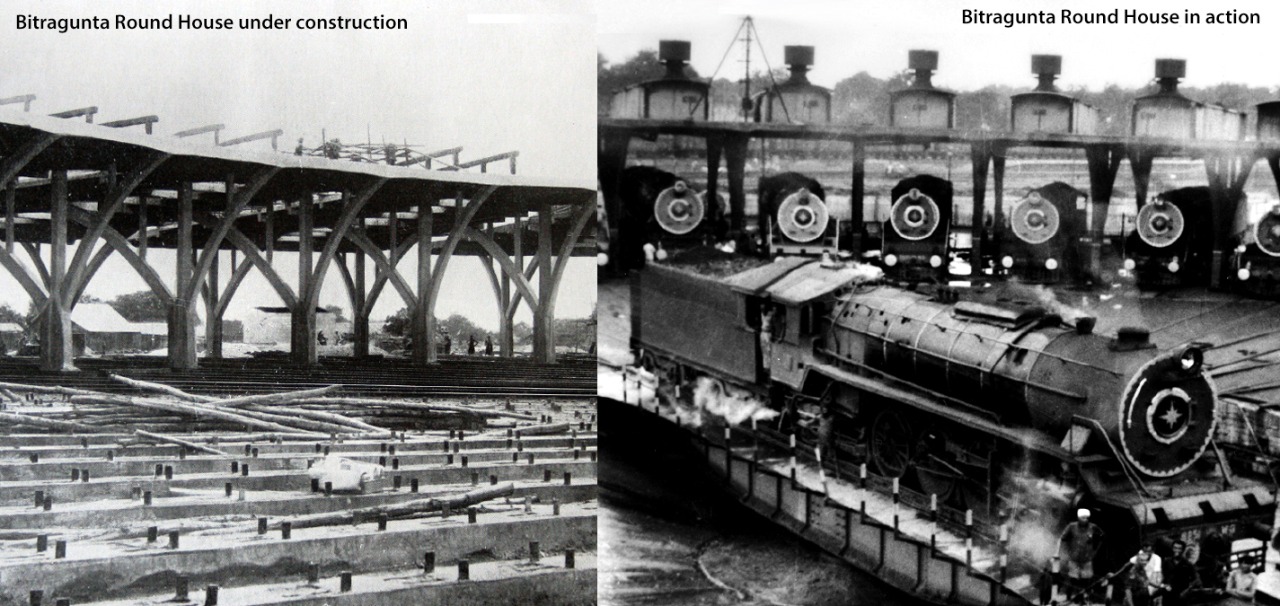
Bitragunta Round House
A steam locomotive shed in Bitragunta, Andhra Pradesh was constructed in 1885. Later in 1934, a roundhouse renowned for its architectural value was added along with a turntable facility. At its peak, Bitragunta shed was one of the biggest in the Railways system handling 22 passengers and 59 goods steam locomotive. The transition in the mode of traction power from steam to diesel and thereafter to electric resulted in the reduction of shed activities. The end to end running of goods trains reduced the marshalling needs and finally led to the closure of Bitragunta loco shed. Consequent to the closure of the steam loco shed in Bitragunta, its sprawling infrastructure has not yet been utilized for alternative purposes leading to its atrophy.
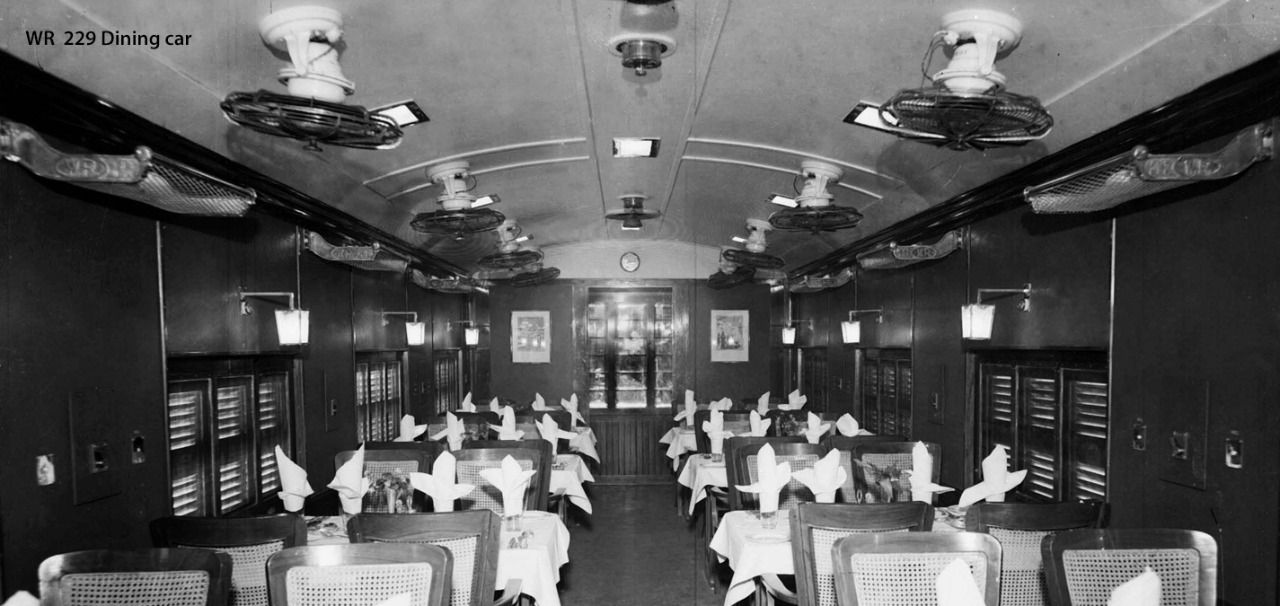

Dining Car
A dining car or a restaurant car is a railroad passenger car that serves meals in the manner of a full-service or sit-down restaurant on the wheels. By the mid-1880s, dedicated dining cars were a normal part of long-distance trains in western countries which eventually got introduced in Indian railways. In the image, this is WR229 Dinning car. In one of the most common dining car configurations, one end of the car contains a galley (with an aisle next to it, so passengers can pass through the car to the rest of the train) while the other end has table or booth seating on either side of a center aisle. Trains with high demand for dining car services sometimes feature "double-unit dining cars" consisting of two adjacent cars functioning to some extent as a single entity.
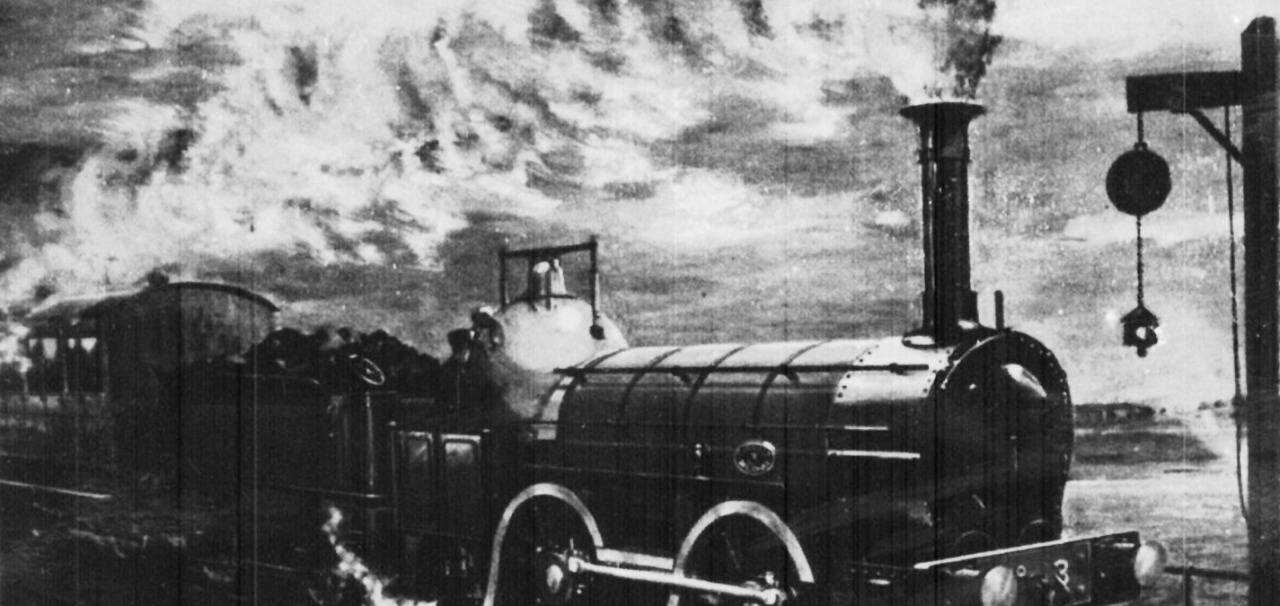

Ball Signal
Railway signalling is a system used to direct railway traffic as it is vital for safe and punctual movements of trains. Train movement safety and efficient management of trains entirely depends on Railway signalling. In the due course of time, many signalling and train control systems have been evolved. One such kind of signal known as ball signal was being introduced in early days for controlling the movement of trains. This is an object like a ball hoisted manually to the top of a track-side pole to indicate that the way was clear for an approaching train. The signal indicates All clear when raised and danger when lowered.








